Multi-AZ vs Multi-Region: Disaster Recovery
Explore the differences between Multi-AZ and Multi-Region disaster recovery strategies to enhance your business's resilience and availability.
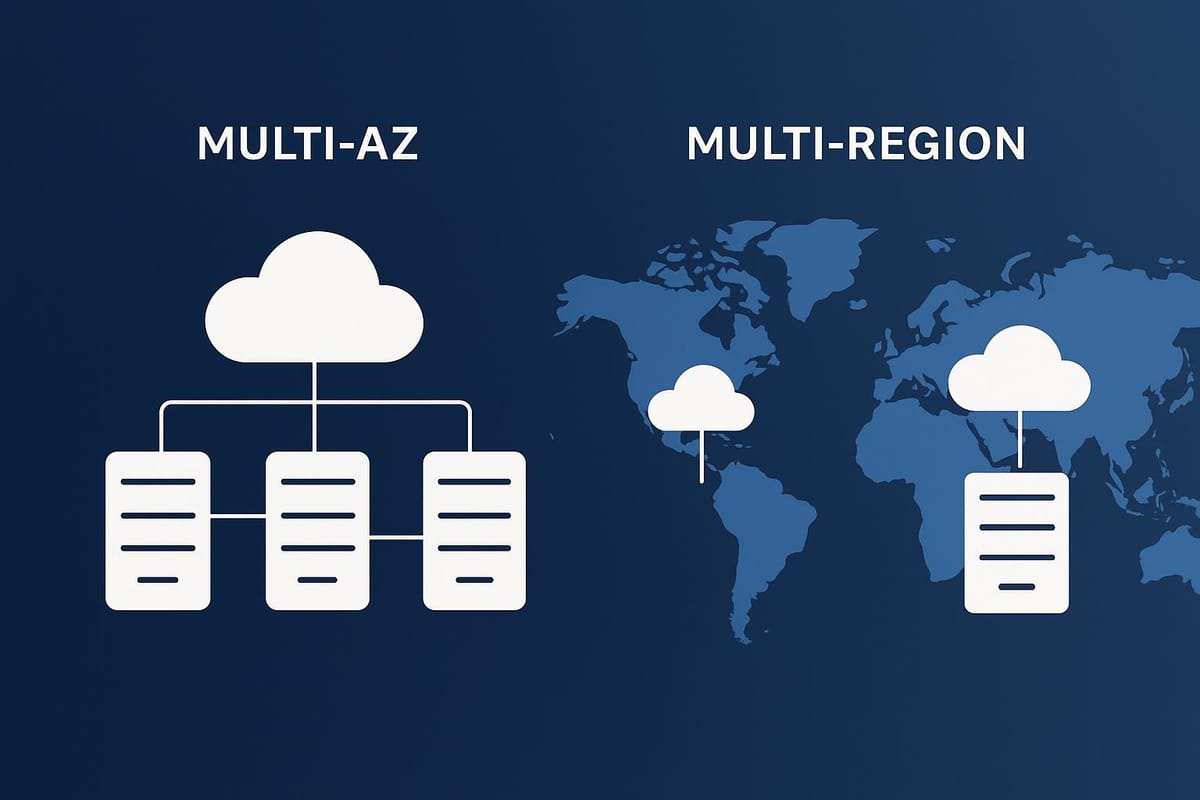
Disaster recovery is crucial for keeping your business running during system failures. AWS offers two main approaches: Multi-AZ and Multi-Region. Here's a quick comparison to help you decide:
- Multi-AZ: Protects against local failures within a single AWS region. It's simpler, faster to recover, and cheaper but can't handle region-wide outages.
- Multi-Region: Protects against large-scale disasters by spreading resources across multiple regions. It offers better resilience but is more complex and costly.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Multi-AZ | Multi-Region |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Single AWS region | Multiple AWS regions |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Easier to set up and manage | More advanced setup required |
| Recovery Time | Faster (minutes) | Slower (hours) |
| Protection Level | Localised failures | Region-wide disasters |
| Latency | Lower due to proximity of zones | Higher due to cross-region distance |
Which should you choose?
- Use Multi-AZ for local resilience on a budget.
- Choose Multi-Region if you need high availability across regions or must meet strict compliance rules.
Start with Multi-AZ for simplicity and scale to Multi-Region as your business grows.
Multi-AZ: Core Components and Limits
Multi-AZ Technical Setup
Setting up a Multi-AZ deployment involves configuring essential components to ensure disaster recovery and system reliability. Key elements include:
- Database Replication: AWS ensures data is synchronised between primary and standby databases across different Availability Zones using synchronous replication.
- Load Balancer Configuration: Application Load Balancers are set up with health checks to monitor the performance of instances and reroute traffic when needed.
- Auto Scaling Groups: EC2 instances are deployed across multiple Availability Zones using Auto Scaling Groups, which automatically manage resource distribution.
Multi-AZ Benefits
Multi-AZ deployments provide several operational advantages:
- Automated Failover: If an Availability Zone encounters issues, AWS automatically redirects traffic to healthy instances in another zone, reducing downtime.
- Data Consistency: Synchronous replication ensures minimal data loss during failovers, helping maintain business operations.
- Simplified Management: AWS handles essential tasks like automated backups, patching, hardware maintenance, and failover processes, freeing organisations to focus on their core activities.
Multi-AZ Constraints
While Multi-AZ deployments offer many benefits, they also have some limitations:
- Regional Boundaries: Multi-AZ protection is limited to a single AWS Region. If an entire region experiences an outage, Multi-AZ alone cannot guarantee service availability.
- Higher Costs: Maintaining redundant infrastructure across multiple zones increases expenses due to additional instances, inter-AZ data transfers, and storage replication.
- Performance Impact: Synchronous replication across zones can introduce slight latency, which may affect applications that require extremely low response times.
| Aspect | Impact on SMBs | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher expenses due to redundant resources | Reserve Multi-AZ setups for critical workloads |
| Latency | Small latency increase from synchronous replication | Use optimisation techniques for latency-sensitive apps |
| Recovery Time | Failovers are quick but not instant | Implement retry mechanisms at the application level |
| Data Protection | Strong data protection with minimal loss | Regularly test and update failover procedures |
Multi-AZ deployments are highly effective for managing localised failures and ensuring business continuity. In the next section, we’ll explore Multi-Region setups, which extend recovery capabilities beyond a single region.
AWS re:Invent 2022 - Multi-Region design patterns and best ...
Multi-Region: Setup and Trade-offs
Unlike Multi-AZ strategies, Multi-Region setups extend recovery capabilities across multiple regions, offering protection against large-scale failures that affect entire geographic areas.
Multi-Region Technical Setup
Setting up a Multi-Region deployment requires careful planning and coordination across regions. Key components typically include:
- Global DNS management: Tools like Route 53 with health checks to route traffic between regions.
- Asynchronous data replication: Ensuring data is copied from the primary to secondary regions.
- Application distribution: Deploying application components across multiple regions.
- Monitoring: Using services like CloudWatch to track metrics and set alarms across regions.
These elements work together to create a resilient system that can handle regional disruptions.
Multi-Region Protection Features
Multi-Region architectures provide several key benefits:
- Geographic redundancy: Protects against regional outages or natural disasters by spreading resources across multiple locations.
- Regulatory compliance: Supports data sovereignty and backup location requirements.
- Performance optimisation: Serves users from the closest region, improving response times.
These features ensure services remain available even during significant disruptions affecting an entire region.
Multi-Region Implementation Hurdles
While Multi-Region setups offer enhanced protection, they come with notable challenges:
-
Technical Complexity:
- Managing cross-region networking and ensuring data consistency.
- Planning and executing cross-region failovers.
-
Operational Challenges:
- Higher operational costs compared to Multi-AZ setups.
- Increased monitoring and maintenance demands.
- Strengthened security for cross-region data transfers.
-
Performance Impacts:
- Increased latency and higher costs for cross-region data transfers.
- Data consistency issues due to asynchronous replication.
Small and medium-sized businesses should carefully evaluate these challenges against their specific needs. Starting with critical workloads in a phased approach can help manage complexity and costs while improving disaster recovery capabilities. Advanced setups should only be pursued when the benefits outweigh the added complexity.
Selecting the Right Option
Choosing the right strategy depends on your business needs, available resources, and how much risk you're willing to take. Below, we break down the scenarios and factors to consider, building on the earlier discussion about infrastructure and costs.
When to Use Multi-AZ
Multi-AZ is ideal for businesses looking for local failure protection without overspending. This option works well if:
- You can handle brief interruptions during failover, with recovery times measured in minutes.
- Data residency rules allow storage within a single region.
- You're balancing a limited budget with reliability needs.
For small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), Multi-AZ is often a more affordable choice, as it requires less infrastructure and is easier to manage.
When to Use Multi-Region
A Multi-Region setup is better suited for more demanding scenarios, such as:
- Meeting strict regulations that require data to be stored across multiple regions.
- Ensuring critical applications experience little to no downtime during failover.
- Serving a widely distributed user base that benefits from localised access.
- Mitigating the risks of regional outages that could severely disrupt operations.
While Multi-Region deployments come with higher costs and added complexity, they can deliver uninterrupted service for businesses where downtime is not an option.
Decision Framework for SMBs
When deciding between these strategies, focus on these key areas:
-
Risk Assessment
Evaluate potential threats and consider both immediate financial losses and the longer-term impact on your reputation. -
Compliance Requirements
Check your industry’s regulations, particularly around data residency and backup policies. Some sectors may require data to be stored in separate geographic locations for disaster recovery purposes. -
Resource Availability
Look at your budget and the technical skills of your team. Multi-Region setups often require advanced expertise in managing distributed systems and come with higher ongoing costs.
For many SMBs, starting with a Multi-AZ deployment and expanding to Multi-Region as your business grows is often the most practical and scalable approach.
Feature Comparison Table
This table highlights the main differences in availability and network performance, focusing on geographic reach and latency, between Multi-AZ and Multi-Region disaster recovery approaches.
| Feature | Multi-AZ | Multi-Region |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Scope | Operates within a single region across multiple availability zones | Spreads resources across multiple, geographically distant regions |
| Network Latency | Typically lower latency due to the close proximity of AZs | Generally higher and more variable latency due to greater distances |
Multi-AZ setups often deliver more consistent performance thanks to reduced latency, while Multi-Region strategies improve availability by distributing risk across regions, though this may come with latency challenges.
Up next, we’ll look at ways to manage costs for these deployments.
Cost Management Guidelines
Managing disaster recovery costs effectively requires careful planning and resource allocation.
Multi-AZ Cost Control
To keep Multi-AZ deployment costs in check, adjust resources based on workload needs:
- Auto-scaling: Scale resources down during low-demand periods to save money.
- Reserved Instances: Lock in lower prices for predictable workloads.
- Storage lifecycle policies: Move rarely accessed data to cheaper storage options.
Multi-Region Cost Control
Deployments across multiple regions are more expensive due to data replication and increased network usage. Here's how to manage these costs:
| Cost Area | Optimisation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer | Reduce costs by using efficient replication methods and fine-tuning network settings. |
| Storage | Limit duplication and reduce storage overhead by optimising data replication. |
| Compute | Run non-critical workloads on Spot Instances to take advantage of lower pricing, even with occasional interruptions. |
These steps help manage multi-region expenses while maintaining system reliability.
AWS Resources for SMBs
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in the UK can cut disaster recovery costs using resources like Critical Cloud's AWS Optimisation Tips blog (https://aws.criticalcloud.ai). Some effective strategies include:
- Adding cost allocation tags for detailed spending insights.
- Setting up AWS Budgets with custom alerts in GBP to track expenses.
- Using AWS Cost Explorer to find areas where savings can be made.
Additionally, tools like AWS Trusted Advisor and automated cost monitoring can help avoid surprise charges.
Summary
Key Comparisons
When deciding between Multi-AZ and Multi-Region disaster recovery, it's important to match your recovery goals with the resources you have available.
| Aspect | Multi-AZ | Multi-Region |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Level | Handles hardware issues and local outages | Protects against large-scale disasters |
| Implementation | Easier to set up with less complexity | Requires a more advanced and complex setup |
| Cost Impact | Lower operational costs | Higher costs due to added complexity |
| Recovery Speed | Quicker recovery (usually minutes) | Slower recovery (typically hours) |
| Geographic Scope | Redundancy within a single region | Protection across multiple regions |
This table highlights the benefits and trade-offs of each option. With these comparisons in mind, you can take steps to refine your disaster recovery plan.
Next Steps
-
Define Recovery Objectives
Clearly outline your Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) to select the right approach. -
Assess Technical Resources
Evaluate your team's expertise to ensure they can handle more advanced setups if needed. -
Start Small and Scale
For many UK-based small and medium-sized businesses, beginning with a Multi-AZ setup is a practical choice. As your business needs grow, you can gradually move to a Multi-Region strategy. For more advice on scaling disaster recovery solutions, check out the AWS Optimization Tips, Costs & Best Practices for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses blog. -
Monitor and Adjust
Regularly track performance and costs. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor can help you manage expenses and identify areas for improvement. Setting alerts in GBP ensures you stay within your budget.
FAQs
What should I consider when choosing between Multi-AZ and Multi-Region disaster recovery strategies for my business?
Choosing between Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) and Multi-Region disaster recovery strategies depends on several factors, including your business needs, budget, and tolerance for downtime.
Multi-AZ strategies are ideal for businesses requiring high availability and minimal latency within a single region. They are cost-effective and provide automatic failover to another availability zone in the same region, making them suitable for most small to medium-sized businesses.
Multi-Region strategies, on the other hand, are designed for scenarios where geographic redundancy is critical, such as compliance requirements or protection against large-scale regional failures. While more expensive, they offer enhanced resilience and the ability to serve users closer to their location.
When deciding, consider factors like recovery time objectives (RTO), recovery point objectives (RPO), data replication costs, and the potential impact of outages on your customers. For tailored advice on optimising your AWS setup, including cost-saving tips for SMBs, consult resources like Critical Cloud’s AWS blog.
What strategies can small and medium-sized businesses use to manage the higher costs of a Multi-Region disaster recovery setup?
Managing the costs of a Multi-Region disaster recovery setup can be challenging for small and medium-sized businesses, but there are effective strategies to optimise spending while maintaining resilience.
- Prioritise critical workloads: Focus on replicating only essential applications and data across regions to reduce unnecessary duplication and storage costs.
- Leverage AWS cost optimisation tools: Services like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Savings Plans can help identify areas to cut costs and predict future expenses.
- Use automation: Automate failover processes to ensure efficient recovery without requiring constant manual intervention, which can save both time and resources.
For further insights on optimising AWS usage, small and medium-sized businesses can explore expert guidance tailored to their needs, such as cost management, architecture design, and performance improvement tips.
What are the key challenges of implementing a Multi-Region disaster recovery strategy, and how can they be resolved?
Implementing a Multi-Region disaster recovery strategy can be complex due to several factors. Data synchronisation between regions is one of the main challenges, as ensuring consistency across geographically distant servers requires robust replication mechanisms. Additionally, latency issues may arise when accessing data or services from different regions, potentially impacting performance.
To address these challenges, you can use AWS services like Amazon RDS Global Database or Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication to simplify data replication. It's also crucial to design your architecture with latency-tolerant applications and implement regular testing of your disaster recovery setup to ensure it performs as expected. Proper planning and monitoring tools can help streamline operations and reduce risks.