Mainframe Assessment: First Step to AWS Migration
A 5–16 week mainframe assessment maps dependencies, estimates costs and creates wave-based migration plans to reduce risk and optimise AWS migration.
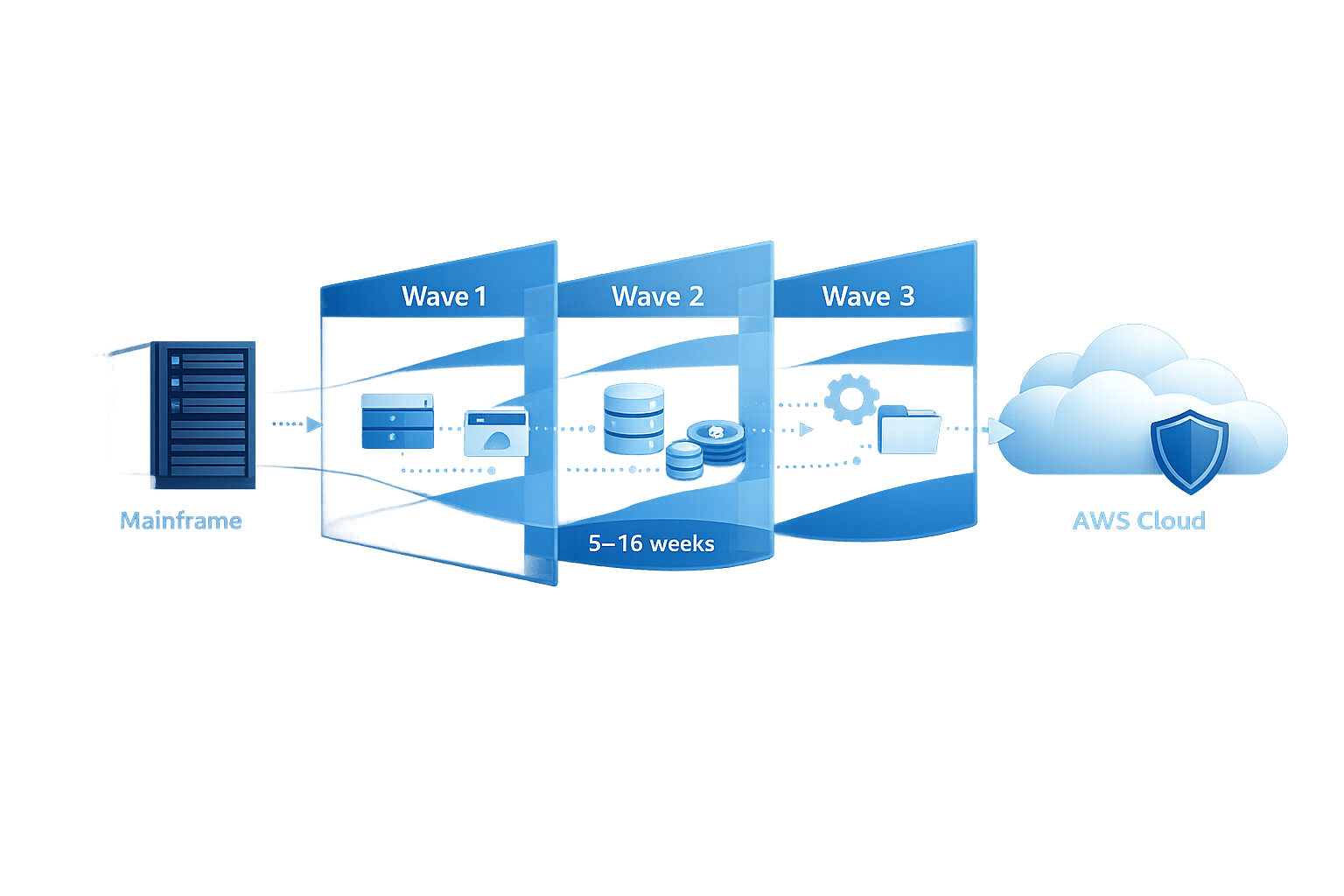
When planning to migrate your mainframe to AWS, starting with an assessment phase is essential. This step helps identify application dependencies, align IT with business goals, and avoid costly errors. The assessment typically lasts 8–16 weeks and categorises applications using the "Seven Rs" framework: Rehost, Replatform, Refactor, Rearchitect, Repurchase, Retain, or Retire. Skipping this phase may lead to project delays, unexpected costs, and technical issues.
Key Takeaways:
- Purpose: Evaluate your mainframe's readiness for migration and define a clear business case.
- Process: Combines technical analysis (code, dependencies) with business alignment.
- Deliverables: Rationalisation scorecards, cost estimates, migration plans, and legacy system documentation.
- Timing: Discovery and assessment occur in the first 5–14 weeks of the migration programme.
- Benefits: Reduces risks, identifies cost-saving opportunities, and ensures a smoother migration.
For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), this phase is especially important to manage limited budgets effectively while ensuring a successful transition to AWS. Skipping the assessment often results in higher costs and greater risks down the line.
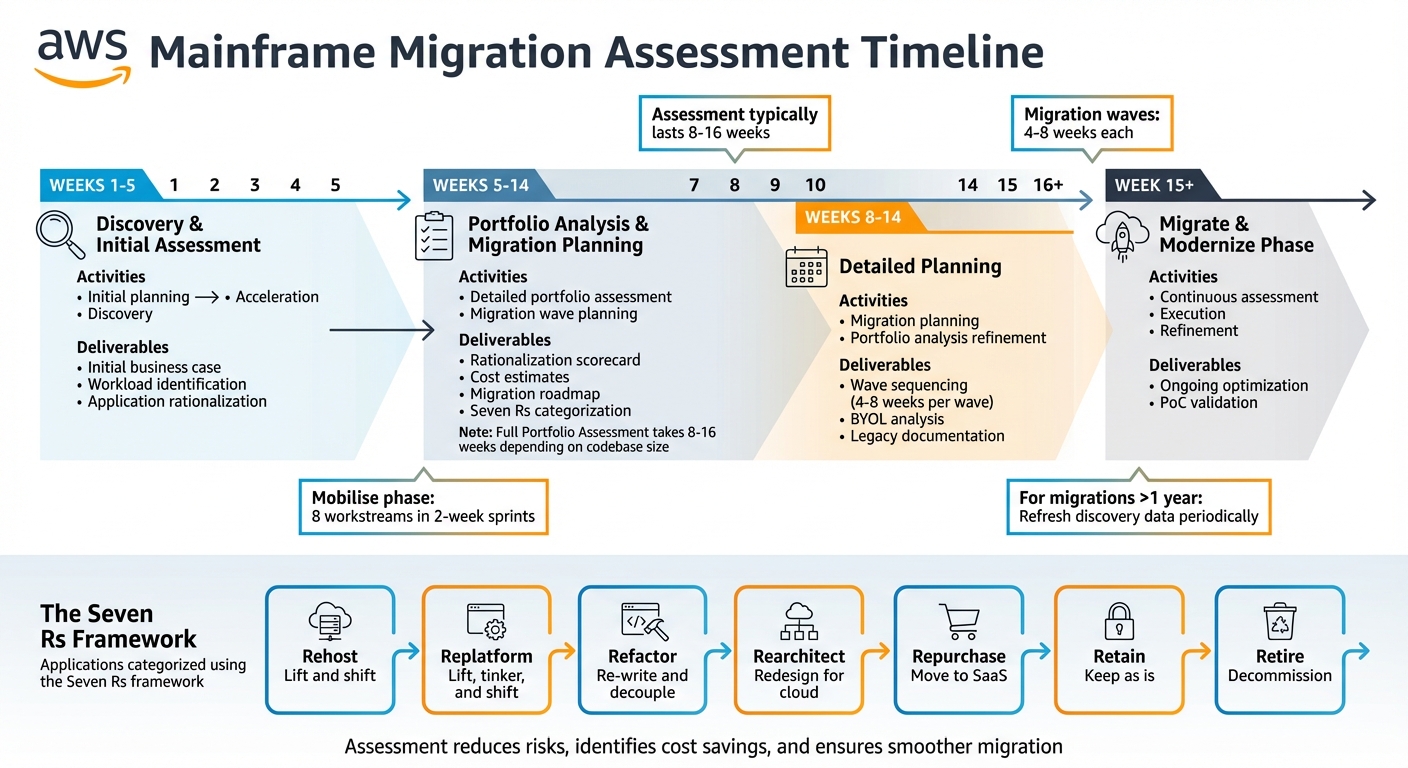
AWS Mainframe Migration Assessment Timeline: 5-16 Week Process Overview
1. Mainframe Assessment
Scope
Mainframe assessments operate on two levels: a top-down Portfolio Assessment and a bottom-up Inventory Assessment. The Portfolio Assessment links business functions to strategic goals, while the Inventory Assessment digs into the technical side, analysing code, dependencies, and data flows. This dual approach ensures both strategic alignment and technical accuracy.
The assessment examines applications across five key areas:
- Business criticality: How essential the application is to operations.
- Technical complexity: Including older languages like COBOL and PL/I.
- Application health: Measured through SLAs and incident history.
- Support levels and data volumes: How well-supported the application is and the scale of its data.
- Documentation quality: The availability and clarity of existing documentation.
For small-to-medium businesses (SMBs) with limited insight into their legacy systems, this process helps pinpoint "quick wins" for migration. These early successes reduce risk and provide faster results by enabling initial cloud experiences. The insights gained shape the deliverables for the migration process.
Deliverables
The assessment produces a rationalisation scorecard that assigns each mainframe application to one of the Seven Rs (e.g., Retire, Retain, Rehost). This is accompanied by an executive summary detailing lines of code (LOC). Applications are grouped and sequenced for migration "waves", ensuring that tightly integrated services move together, which simplifies the transition process.
Other deliverables include:
- Cost estimates for services like Amazon EC2, Amazon EBS, and storage.
- A BYOL (Bring Your Own Licence) analysis to optimise dedicated host mappings and reduce licensing fees.
- Legacy system documentation, which addresses the risk of losing expertise as mainframe experts retire.
These outputs establish a clear timeline and roadmap for migration planning and execution.
Timing
The initial phases of discovery, acceleration, and planning typically occur within the first five weeks of a migration programme. A full Portfolio Assessment usually takes between 8 and 16 weeks, depending on the size of the codebase and the number of applications. Migration planning and portfolio analysis generally take place between weeks 8 and 14.
For long-term migrations (over a year), it's important to periodically refresh discovery data. This ensures migration plans remain accurate and effective. Automated tools can significantly speed up the process, supporting assessments for up to 30,000 servers in a single job.
Cost Focus
While these assessments require upfront investment in workshops, interviews, and tools, they quickly uncover cost-saving opportunities. For example, they help determine whether to retire unused applications or refactor critical ones, avoiding costly mistakes.
The recommendations also focus on optimising infrastructure, enabling organisations to shift from fixed legacy costs to pay-as-you-go models. This approach aligns spending with actual usage. Over time, this transition opens the door to capabilities like advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning - areas that are harder to achieve with on-premises systems.
2. Discovery in 10-Step AWS Migration
Scope
Discovery is the foundation of any AWS migration process. It sets the stage for every decision that follows - whether it’s selecting migration patterns, organising workloads into waves, or estimating costs. Without precise discovery data, organisations risk service outages, performance bottlenecks, and expensive rework caused by overlooked interdependencies.
The process involves gathering critical metadata, including details about the source portfolio, target environment specifications, and wave planning. This information helps assess mainframe workloads, their dependencies, and interface requirements. Discovery also highlights key drivers behind the migration, such as looming data centre exit deadlines or hardware nearing end-of-support. These insights form the backbone of the migration strategy, steering the process towards well-informed decisions.
Deliverables
Within the first 1–5 weeks, discovery yields an initial business case, identifying which workloads are ready for migration and rationalising them. From there, a detailed migration roadmap is developed, categorising applications based on the Seven Rs framework: Rehost, Replatform, Refactor, Retire, Retain, Repurchase, and Relocate. Automated tools further simplify the process by estimating costs for Amazon EC2 and EBS, analysing Bring Your Own Licence (BYOL) options to cut licensing expenses, and flagging over-provisioned instances.
Another crucial outcome is the identification of waste - like unused code, duplicate components, or inactive datasets - that can be excluded from the migration scope. This step is especially helpful for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) operating on tight budgets. Each deliverable is crafted to streamline decision-making and optimise migration planning.
Timing
The discovery phase kicks off with initial planning during the first five weeks. This is followed by detailed assessments and the creation of a migration roadmap in the weeks that follow. During the mobilise phase, activities are typically organised into eight workstreams, each spanning two-week sprints. From week 15 onwards, continuous assessment and refinement take place, running through to the end of the migration programme.
Cost Focus
While the discovery phase requires upfront investment, it quickly reveals opportunities for cost savings. The AWS Migration Acceleration Programme (MAP) offers tools, best practices, and financial incentives to help offset the initial costs of assessment. Additionally, SMBs can collaborate with AWS Competency Partners, who provide fixed-price assessments to prevent scope creep and avoid unexpected consulting fees. This cost-conscious approach ensures that every penny spent during discovery contributes to a more efficient migration process.
"A well-planned and executed assessment is the cornerstone of any successful mainframe migration strategy." - Yesh Singhal, mLogica V.P. of Strategic Solutions and Services
3. Portfolio Analysis for Application Rationalisation
Scope
After the discovery phase, portfolio analysis takes a deeper dive into the mainframe estate by collecting data on applications, infrastructure, and business operations. This step goes beyond just identifying components - it evaluates both active and inactive elements, mapping applications to their infrastructure while also factoring in non-technical dependencies like operational needs. Each application's criticality, complexity, health, support, and documentation are thoroughly assessed. This is especially vital given that mainframe applications often involve millions of lines of legacy code. The insights gained here are pivotal for shaping an informed migration strategy.
Deliverables
The portfolio analysis phase delivers several key outputs, including:
- A detailed inventory of applications.
- A high-level migration strategy tailored to each application.
- A migration wave plan.
- An application rationalisation report.
Each application is categorised into one of the "Seven R's" (Rehost, Replatform, Refactor, Rearchitect, Repurchase, Retain, or Retire) to determine its future disposition. This stage also provides an executive summary of code analysis and groups applications based on their interdependencies. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) with limited budgets, this process can highlight immediate cost-saving opportunities by flagging inactive components and redundant applications that can be excluded from the migration scope.
"Application rationalisation is the process of identifying all applications running on the mainframe and determining their target disposition, such as Rehost, Replatform, Refactor, Rearchitect, Repurchase, Retain and Retire – these migration patterns are commonly referred to as the Seven R's."
Timing
Portfolio analysis and migration planning typically occur between weeks 8 and 14 of the migration programme. A complete portfolio assessment for mainframe environments usually takes 8–16 weeks, depending on the size of the code base and the number of applications. Migration waves, which are planned during this phase, generally last 4–8 weeks. However, the assessment doesn’t end here - it transitions into the "Migrate and Modernise" phase from week 15 onwards, where further optimisation takes place.
Cost Focus
This analysis moves away from generic benchmarks and instead uses actual utilisation data to provide accurate AWS run rate estimates. Automated tools factor in real-time Amazon EC2 pricing and host configuration details to produce precise cost projections. For SMBs, adopting simpler strategies like Rehost or Replatform can deliver quick cost efficiencies, allowing savings to be reinvested into more complex modernisation initiatives. However, the analysis also identifies potential risks, such as the challenges and increased costs that arise from combining different migration patterns.
For SMBs looking to dive deeper into AWS cost-saving strategies, additional insights can be found in the guide on AWS Optimisation Tips, Costs & Best Practices for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses.
4. Proof of Concept in Mainframe Modernisation
Scope
Once the portfolio analysis is complete, the next step is to validate the chosen migration strategy through a Proof of Concept (PoC). This step focuses on testing the most technically challenging aspects of a mainframe workload to ensure the selected tools and architecture deliver as expected. The PoC scope typically includes evaluating batch processing durations, managing complex programme and data dependencies, and addressing high-throughput demands. For example, it may involve testing batch I/O intensity, transaction volumes (measured in transactions per second), and integrations with satellite or partner systems [25, 26]. This is a critical step to confirm the migration approach is sound before committing significant resources.
Deliverables
The PoC generates several key outputs, such as a validated technical architecture, a refined migration plan, and a report confirming functional equivalence [25, 3]. These deliverables allow teams to adjust the TCO model and fine-tune the migration roadmap based on real-world results [1, 3]. Additionally, lessons learnt during this pilot phase feed into the Cloud Centre of Excellence (CCoE), helping refine strategies for security, compliance, and account governance. For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), this step reduces unexpected challenges later on and provides a clearer picture of the migration's actual cost and outcomes.
"Projects can fail when selected tools and the proposed architecture don't address the most complex technical aspects of a mainframe workload."
Timing
The PoC is conducted during the Mobilise phase, which comes after selecting the tools but before diving into full-scale modernisation (Step 6 of the 10-step approach). Pilots during this phase allow teams to refine the business case, migration roadmap, and operational model based on the findings. Testing critical aspects early - before entering the Migrate and Modernise phase - prevents costly setbacks caused by unresolved technical issues. This proactive validation ensures a smoother transition to the full-scale modernisation phase.
Cost Focus
One of the benefits of the PoC is shifting costs away from fixed mainframe expenses to AWS’s pay-as-you-go model, aligning spending with actual usage. By identifying cost-saving opportunities and addressing technical bottlenecks upfront, the PoC reduces the likelihood of expensive failures later [1, 3]. For instance, AWS Mainframe Modernisation utilities like M2SFTP and TXT2PDF can help eliminate legacy licensing fees. For SMBs with limited budgets, starting with low-risk, less complex applications can build internal confidence while keeping costs under control. For further guidance on AWS cost optimisation tailored to SMBs, check out AWS Optimisation Tips, Costs & Best Practices for Small and Medium Sized Businesses (https://aws.criticalcloud.ai).
AWS re:Invent 2024 - Modernize mainframe applications faster using Amazon Q Developer (DOP221-NEW)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Starting with a mainframe assessment as the first step in an AWS migration can offer a solid framework for success, but it also comes with potential drawbacks that small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) should carefully weigh. The assessment phase sets the stage for the entire migration process by aligning technology, processes, and business goals. It builds a business case rooted in data, uncovers hidden dependencies, and avoids the common pitfall of undefined project scope halfway through large migrations. However, the time commitment of 5–14 weeks can become a drawback if migration efforts stretch beyond a year without refreshing the discovery data.
Key Benefits of a Mainframe Assessment
One of the biggest advantages is reducing risks. By identifying application dependencies and system relationships early on, businesses can better plan migration waves and avoid unexpected production issues. Assessments also reveal shadow IT and unaddressed security or network needs, which might otherwise disrupt the migration process.
That said, focusing solely on technical aspects during the assessment can overlook challenges like team resistance or skill gaps, especially if mainframe teams are not involved. Another hurdle is the lack of documentation for many mainframe systems, which can leave automated tools unable to capture the complex business rules hidden in legacy code. Despite these challenges, the insights gained from assessments are critical for making informed decisions about costs and resource allocation in later phases.
Cost and Time Considerations
From a financial standpoint, assessments help businesses spend smarter. They allow for licensing evaluations and right-sizing strategies, enabling organisations to make the most of AWS's pay-as-you-go pricing model. Using AWS Transform jobs, businesses can analyse up to 30,000 servers in a single run, providing detailed cost estimates for Amazon EC2, EBS, and storage. However, the upfront time investment can be a sticking point for SMBs looking for quicker results. While skipping the assessment might seem like a shortcut, it often leads to reactive planning, higher infrastructure costs, and technical debt.
Comparing Approaches: Assessment vs. Skipping It
The table below outlines the differences between conducting a mainframe assessment and bypassing this step:
| Feature | Mainframe Assessment (First Step) | Skipping Assessment Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Clearly defined; uncovers shadow IT and hidden dependencies | Often undefined; prone to "surprises" mid-migration |
| Deliverables | TCO analysis, high-confidence wave plans, validated inventory | Reactive runbooks, unvalidated migration patterns |
| Timing | Structured (5–14 weeks for full portfolio analysis) | Immediate start, but delays likely due to unforeseen blockers |
| Cost Focus | Optimised via BYOL analysis and right-sizing | High technical debt, unoptimised infrastructure spend |
| Risk Level | Low; dependencies and security gaps identified early | High; critical requirements often missed until production issues arise |
Striking a Balance
Balancing thorough preparation with flexibility is crucial. As AWS guidance highlights:
"The analysis informs the process, reduces risk and cost, aligns business and IT priorities, and accelerates business outcomes".
For SMBs working with tight budgets, a thorough initial assessment - viewed as an ongoing process rather than a one-off task - provides the best chance for a smooth and cost-effective migration.
Conclusion
Mainframe assessment lays the groundwork for a successful AWS migration. Without it, organisations risk diving into migration blind, potentially overlooking hidden dependencies, undocumented business logic, or the millions of lines of legacy code that underpin critical operations. As AWS experts German Goncalves and Mark Berner explain:
"Assessment activities are critical for any business embarking on long-running cloud programs because the nature of that journey involves risk and cost. It is not only applications that are moving to the cloud, it is the business itself being transformed".
The assessment process, as discussed earlier, offers more than just clarity - it provides a way to control costs and align IT strategies with business objectives. By rationalising applications through assessment, SMBs can categorise workloads using established migration frameworks. This prevents overspending on unnecessary infrastructure and uncovers immediate opportunities for cost savings. Such an approach avoids reactive planning, which often leads to technical debt, and ensures IT remains in sync with broader organisational goals.
If your organisation lacks visibility into its applications - what’s active, how they’re interconnected, or their ideal cloud disposition - a Portfolio Assessment is crucial. This becomes even more pressing when legacy experts retire, potentially taking decades of institutional knowledge with them. Structured assessment workshops can help bridge this gap, ensuring continuity and reducing risks.
While the time investment for assessment may seem significant, skipping this step almost always leads to higher costs and disruptions later. A structured assessment creates high-confidence migration wave plans, enabling logical grouping of applications, preserving critical integrations, and ensuring smooth business operations throughout the transition. For organisations navigating complex mainframe environments or operating under tight budgets, assessment isn't just helpful - it’s the most sensible step to take before migrating any workloads to AWS.
FAQs
What are the 'Seven Rs' of mainframe migration to AWS?
When it comes to moving and updating mainframe applications on AWS, the 'Seven Rs' offer a structured set of strategies. Each approach caters to different needs, allowing businesses to select the most suitable path for their migration journey:
- Rehost: Often called lift-and-shift, this involves moving applications to the cloud with minimal changes. It’s a straightforward way to get started quickly.
- Replatform: This strategy makes small adjustments to applications, optimising them to perform better in a cloud environment without overhauling their core structure.
- Refactor: Here, the application’s architecture is modified to take full advantage of cloud-native features, enhancing performance and scalability.
- Rearchitect: This involves redesigning applications entirely to align with new business goals or requirements, ensuring they remain relevant and effective.
- Rebuild: Starting from scratch, this approach involves rewriting applications using modern tools and technologies to create a future-ready solution.
- Replace: Legacy applications are swapped out for ready-made, off-the-shelf solutions, eliminating the need for custom development.
- Retire: Applications that are no longer useful or cost-effective are decommissioned, reducing unnecessary overhead.
By evaluating these strategies, businesses can identify the best approach to ensure a smooth migration process while achieving cost savings and improved scalability on AWS. Each option offers a tailored solution, depending on the application’s current state and the organisation’s goals.
Why is the assessment phase critical for reducing risks in an AWS migration?
The assessment phase plays a key role in reducing risks during an AWS migration. It involves a thorough review of your existing applications, infrastructure, and their dependencies. This step helps pinpoint potential challenges early, giving you the chance to address them before they escalate into bigger problems during the migration process.
By evaluating your system's readiness and resolving any gaps ahead of time, businesses can create a more seamless transition to AWS. This proactive approach helps to avoid unexpected delays or disruptions, which can be both time-consuming and expensive. Additionally, the insights gained during this phase enable smarter decision-making, ensuring the migration strategy is aligned with the organisation's long-term objectives.
Why is a mainframe assessment important for small and medium-sized businesses planning an AWS migration?
A mainframe assessment plays a crucial role for small and medium-sized businesses. It offers a detailed look at your current applications, their dependencies, and your overall IT setup. This understanding is key to planning a seamless migration to AWS, helping you avoid unnecessary risks and unexpected expenses.
By spotting potential hurdles early on, businesses can create a customised modernisation plan that aligns with their objectives. This ensures a transition to the cloud that is both cost-efficient and scalable, setting the stage for leveraging AWS's features to drive growth and improve operations.